
Apache Arrow is an in-memory data structure handling complex types with flat tables as well as JSON like data specification for building data systems. Developers can create very fast algorithms which process Arrow data structures. It helps Efficient and fast data interchange between systems without the serialization costs.A columnar memory-layout permitting O(1) random access. The layout is highly cache-efficient in analytics workloads and permits SIMD optimizations with modern process.
Arrow is a component used to accelerate analytics within a particular system and to allow Arrow-enabled systems to exchange data with low overhead. For the Python and R communities, Arrow as data interoperability helps to resolve roadblocks to tighter integration with big data systems
Advantages of a Common Data Layer
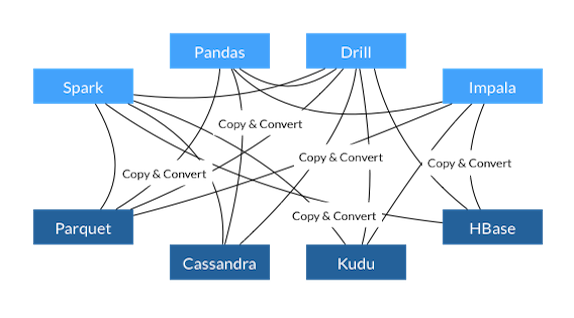
- Each system has its own internal memory format
- 70-80% computation wasted on serialization and deserialization
- Similar functionality implemented in multiple projects
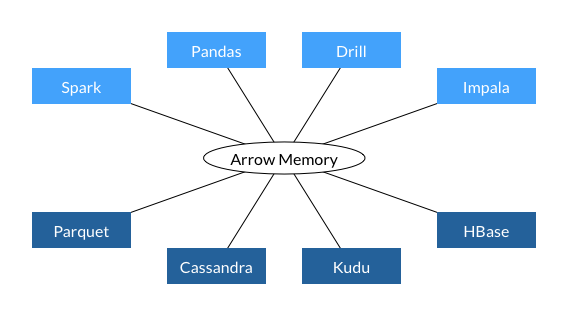
- All systems utilize the same memory format
- No overhead for cross-system communication
- Projects can share functionality (eg, Parquet-to-Arrow reader)
Moving Data Efficiently Between Systems
In the Apache Hadoop ecosystem, the data is often stored in one of the following ways:
- Binary format or a text format
- An online storage system for structured data similar to Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase, or Apache Kudu
The in-memory data structures within each computation system are very specific to that system/application. Hence the adapter code converts to and from file formats and marshals data to and from the wire-protocol formats of the online storage systems. Arrow improves the performance for data movement within a cluster in these ways:
- Two processes utilizing Arrow as their in-memory data representation can “relocate” the data from one process to the other without serialization or deserialization. For example, Spark could send Arrow data to a Python process for evaluating a user-defined function.
- Arrow data can be received from Arrow-enabled database-like systems without costly deserialization on receipt. For example, Kudu could send Arrow data to Impala for analytics purposes.




Leave a comment